-
桤木(Alnus cremastogyne)是国产桤木属11个种中最重要的一个特有种,树高可达40 m,主要分布在四川成都平原及周边山地,是人造板、造纸及建筑、家具的良好用材[1, 2]。桤木为非豆科固氮树种,同时也是造林绿化、营建生态公益林的先锋树种[3]。2018年,我国进口木材及木制品总金额达261.36亿美元(不含纸及纸制品),木材供需缺口较大,人工林培育的需求也相应的有所提高,因而对具有优良遗传品质的良种需求也大。而当前我国林木良种选育工作主要集中在主栽用材林和经济林树种,而对于乡土阔叶树种良种选育的研究相对较为落后,基础较差。在早期阶段,王军辉等[4, 5]以桤木自然分布区种源的生长、材性和果实等性状研究了桤木的地理变异及其趋势,并划分了种源区;同时分析了四川种源桤木在湖北、江西和福建的单株生物质产量的遗传变异规律,并初选出5个作为工业用材林的优良种源。杨春惠等对18个桤木种源126个家系进行苗期生长早期选择,筛选出5个适宜在湖北推广发展的优良种源。在保护生态环境的基础上,发展人工林,增加林产品产量和种类,是绿水青山就是金山银山的有效体现[6]。在天然林全面禁伐以保护天然林资源的环境下,为现代林木遗传改良提出了新的更高的要求,就是要实现良种化造林,以最少的人工林面积提供数量更多、质量更好的林产品。
本研究你通过对桤木18个种源(98个半同胞家系)遗传测定林生长表现的测定,分析种源家系遗传变异,以筛选优良的种源/家系,为四川省乡土阔叶用材林和生态防护林培育提供理论基础。
HTML
-
桤木遗传测定林位于四川省资阳市雁江区雁江镇(104°34′35.91″E,30°7′19.37″N)。属盆周浅丘地貌,气候温和,年均温17.3 ℃,年均降雨量965.8 mm,海拔在390~460 m之间。
-
2010年在四川省全分布区内收集桤木种源18个,家系98份(见表1)。2011年3月在四川省林业科学研究院唐昌现代林业基地培育造林苗木,2012年春造林,试验林按5株小区,4个区组重复的随机区组设计营建,株行距为2×3 m。2018年底测定树高、胸径、东西冠幅、南北冠幅和枝下高。
序号No. 种源Provenance 家系号Family No. 经度Longitude/° 纬度Latitude/° 海拔Elevation/m 1 通江Tongjiang 1~5 107.311063 31.987513 406 2 南江Nanjiang 6, 8~13 106.63197 31.941456 738 3 巴州Bazhou 14~20 106.80685 31.703781 368 4 平昌Pingchang 21~26 107.227206 31.605659 532 5 宣汉Xuanhan 28~32,34~36 107.653044 31.456252 482 6 万源Wanyuan 38~39 107.81652 31.990971 591 7 峨眉Emei 41, 42, 45~47 103.366611 29.597917 650 8 沐川Muchuan 49~58 103.639806 29.184222 601 9 剑阁Jiange 61, 62, 64~66 105.508083 32.139917 800 10 泸定Luding 67~70, 72~77, 80 102.205667 29.849361 1 303 11 盐亭Yanting 84~90 105.273694 30.257694 462 12 宝兴Baoxing 92 102.826111 30.371944 1 518 13 金堂Jintang 94~105 103.523056 30.733333 760 15 天台Tiantai 106~112, 114, 115 103.158194 30.311333 840 16 叙舟Xuzhou 117 104.516014 28.647439 471 17 珙县Gongxian 118 104.701557 28.42416 539 19 黔江Qianjiang 120 108.736038 29.417112 1 005 20 茂县Maoxian 123 103.723164 31.565646 1 583 Table 1. Geographic information of provenances or families of A. cremastogyne
-
SPSS软件进行巢氏方差分析,估算区组、种源、家系、种源×区组、家系×区组的方差分量。参照Gilmour等[7]的方法估算种源重复力和家系遗传力。参照洪舟等[8]的方法估算遗传变异系数和表型变异系数。R语言的cor函数计算性状间的遗传相关,采用指数选择法筛选优良种源/家系,并估算优良种源/家系的遗传增益[9, 10, 11]。
1.1. 试验地概况
1.2. 试验材料与设计
1.3. 统计方法
-
7 年生桤木平均树高(H)、胸径(DBH)、冠幅(P)和枝下高(hB)分别为10.0 m、9.0 cm、2.8 m和2.5 m,其变异系数分别为0.19、0.26、0.28和0.46。桤木H平均年增长量为1.4 m,DBH年平均增长量为1.3 cm(见表2)。方差分析结果表明,桤木生长性状在家系水平存在极显著差异,P和hB在种源水平存在极显著差异,种源间树高生长差异显著,表明开展种源选择有望获得较高的遗传增益。
性状 Traits 平均值 Mean 标准差 SE 变异系数
Coefficient of variation方差来源 Source of variation 区组 Block 种源 Provenance 家系 Family H 10.0 1.9 0.19 12.734** 1.831* 3.070** DBH 9.0 2.3 0.26 11.317** 1.456 2.079** P 2.8 0.8 0.28 17.243** 2.107** 2.824** hB 2.5 1.2 0.46 18.942** 4.917** 4.928** H:树高,DBH:胸径,P:冠幅,hB:枝下高,*和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平下差异显著
H: Tree height, DBH: Diameter of breast height, P: Crown width, hB: Clear bole height. * and ** indicate significant differences at the level of 0.05 and 0.01, respectively.Table 2. Phenotypic performance and variation analyses of growth traits of A. cremastogyne
-
桤木生长性状在表型和遗传水平上均存在不同程度的变异,其表型变异系数为0.113(P)~0.303(DBH)之间,遗传变异系数介于0.033(P)~0.369(hB)之间(见表3)。各性状的种源重复力、家系遗传力分别为0.775(DBH)~0.836(H)和0.828(hB)~0.867(H),表明各生长性状在种源/家系水平上均受到较高的遗传控制。
性状
Traits表型变异系数
Phenotypic variation coefficient遗传变异系数
Genetic variation coefficient种源重复力
Provenance repeatability家系遗传力
Family heritabilityH 0.175 0.056 0.836 0.867 DBH 0.303 0.064 0.775 0.841 P 0.113 0.033 0.791 0.857 hB 0.264 0.369 0.832 0.828 H:树高,DBH:胸径,P:冠幅,hB:枝下高
H: Tree height, DBH: Diameter of breast height, P: Crown width, hB: Clear bole heightTable 3. Genetic parameters of growth traits of A. cremastogyne
-
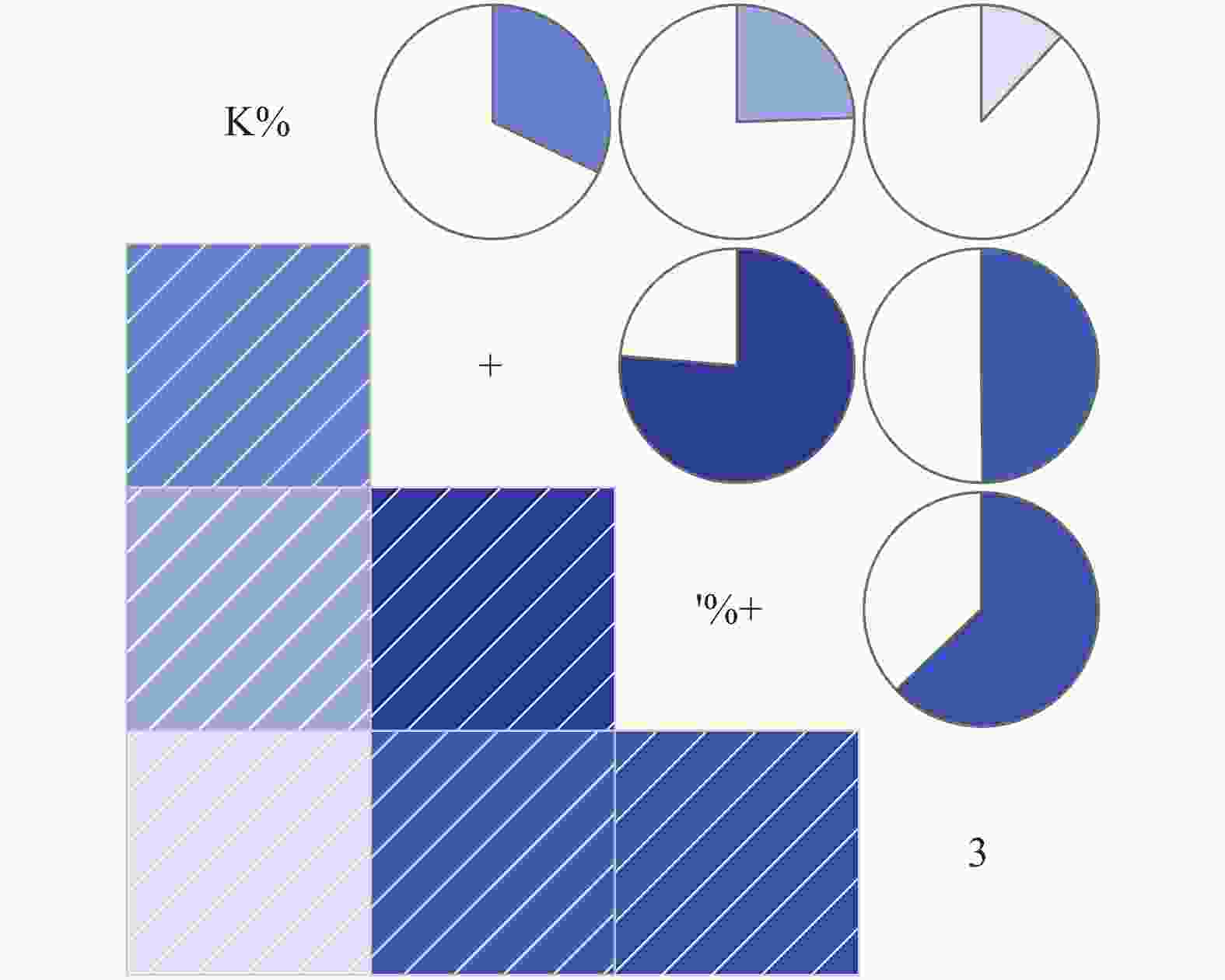
由图1可知,所有性状间均为正相关关系,hB和P之间的相关性最弱,仅0.12;H和DBH之间的相关性最强,为0.71。hB与H、DBH和P之间的相关性均较弱,它们之间关联程度很低。H、DBH和P三个性状间均具有较高的相关性,它们之间的关联程度较高。
-
以H、DBH、P和hB为指标开展优良种源/家系的选择,种源平均聚合性状指数(I)为11.84,以I值大于平均值+1个标准差(12.75)为入选标准筛选出2个优良种源:4号和15号(见表4)。优良种源H、DBH、P和hB的平均遗传增益分别为4.60%、7.23%、5.28%和14.87%。为进一步比较优良家系的选额结果,以H、DBH、P和hB为指标构建家系的聚合性指数,平均为12.51,以I值大于平均值+1个标准差(14.24)为入选标准筛选出8个优良家系,入选家系的H、DBH、P和hB的平均遗传增益分别为9.31%、13.73%、18.24%和28.75%。入选的优良家系分散在7个种源中,仅11号种源有2个家系入选。
类别
Type种源号
Provenance No.家系号
Family No.聚合指数I ΔGH/% ΔGDBH/% ΔGP/% ΔGhB/% 种源选择
Provenance selection4 13.19 6.20 7.69 8.99 15.25 15 12.72 3.00 6.78 1.57 14.49 家系选择
Family selection3 16 14.43 19.66 14.26 9.86 3.36 4 21 14.69 3.33 7.33 21.38 46.15 9 65 15.20 8.35 22.62 26.14 29.62 10 67 14.53 2.22 1.68 36.42 30.28 11 86 15.42 18.46 34.03 21.11 2.79 11 90 14.40 5.53 6.95 1.75 59.15 13 94 14.33 8.61 9.66 20.34 9.52 15 109 14.88 8.36 13.33 8.94 49.12 ΔGH:树高遗传增益,ΔGDBH:胸径遗传增益,ΔGP:冠幅遗传增益,ΔGhB:枝下高遗传增益
ΔGH: Genetic gain of H, ΔGDBH: Genetic gain of DBH, ΔGP: Genetic gain of P, ΔGhB: Genetic gain of hBTable 4. Genetic gain of different traits of selected provenances or families
2.1. 桤木种源/家系生长性状的变异分析
2.2. 桤木生长的遗传变异
2.3. 性状间遗传相关分析
2.4. 优良种源/家系选择
-
从较大区域跨度范围收集优良资源,根据育种目标筛选优良的种源、家系、单株,是培育适宜的推广栽培林木品种的主要途径[12, 13]。本研究从四川省内桤木全分布区广泛收集了现存的桤木优良种质资源,开展种源/家系遗传测定,以充分利用、挖掘其育种潜力。桤木生长变异较大,种源、家系间均存在显著差异,家系间生长性状的差异明显大于种源间,生长最优的16号家系H、DBH、P和hB平均值分别为最差家系的2.2、2.5、2.1和2.6倍,生长最优的11号种源的H、DBH、P和hB平均值分别为最差种源的1.2、1.3、1.3和2.1倍。进一步揭示出桤木种源和家系生长性状选择的潜力较大,对家系的选择潜力高于种源。桤木生长性状年平均生长速率为1.4 m(H)和1.3 cm(DBH),较湖北、江西和福建地区引种栽培的桤木年平均生长速度快[3]。在林木中,由于树高、胸径和材积性状的功能有关联,三者之间必然呈强度遗传相[14]。本研究中,桤木的树高和胸径指标相关系数最高(0.71),与多数研究结果一致。另外,桤木的胸径和冠幅性状的相关系数也较高(0.64),为0.64,表明对桤木树高性状的选育可能将使树高、胸径和冠幅3个性状都获得遗传增益。
遗传变异是由遗传和环境因素决定的,某个树种的遗传和变异决定了其改良效果的优劣[15]。桤木生长性状的种源重复力分别为0.775~0.836,家系遗传力分别为0.828~0.867,表明桤木生长性状受到较高强度的遗传控制。因此,开展桤木优良种源和家系的选择是可行的。王军辉等[16]对桤木生长的适应性和遗传稳定性分析结果揭示,6年生和14年生的树高生长相关显著,对桤木进行早期选择是可靠的。利用综合指数选择法,综合分析生长各性状,4号(平昌)和15号(天台)种源多形状聚合指数值高于优良种源入选标准,入选的8个家系分别来自巴州、平昌、剑阁、盐亭、泸定、金堂和天台种源,表明桤木具有极大的种源/家系选择潜力。该选择结果与杨春惠等[3]在湖北、江西和福建,王军辉等[16]在福建、湖北、湖南、江西和四川多点试验优良种源/家系选择结果相类似,金堂、平昌、天台和盐亭的种源均表现出极大的种源和家系选择潜力。集约经营追求的永远是第一生产力,往往不过多的考虑遗传多样性水平的高或低[16]。如果只选择1个种源,则预期H和DBH遗传增益为6.20%和7.69%;若只选择1个家系,则预期H和DBH遗传增益为14.43%和19.66%。如果兼顾生产力和林分的稳定性,最好选择最好的2~3个种源,H和DBH平均遗传增益为4.60%和7.23%,5~6个家系,H和DBH平均遗传增益为14.85%和10.40%。
桤木速生期在10~15年,本试验林观测数据仅为7年,后续应加强对试验林分的管理和抚育,并做好观测记录工作,以期进一步筛选出生长和材性性状兼优的优良种源、家系或单株。





















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: