-
山苍子(Litsea cubeba (Lour. ) Pers.)别名山胡椒、木姜子,属樟科木姜子属植物,广泛分布于我国长江以南地区,是我国特色木本精油植物资源[1]。山苍子油是一种从山苍子果实的果皮中分离出来的具有怡人的芳香气味淡黄色植物精油[2],具有抗菌[3-4]、抗氧化[5]、抗炎[6]、驱虫[7]等作用,且被允许添加到食品,使其在日用化工、香料、食品、制药等领域具有广泛的应用前景[4,8,9]。山苍子精油主要由单萜类化合物(94.4%~98.4%)构成,其中特征成分为橙花醛(Z-柠檬醛)和香叶醛(E-柠檬醛)这两种顺反异构体组成柠檬醛,含量在60%~80%[10-11]。山苍子精油的成分和含量随产地、生长条件和采收季节的影响均会发生变化[12-13],在精油贸易和加工过程中获取山苍子精油成分含量和组成的具体信息具有重要意义。在前人的研究中,定量分析大多采用峰面积归一化法确定其中成分的相对含量[14-15],但其前提是假设所有成分均出峰,同时根据峰面积积分方式的不同,其相对含量也会发生变化,因此对于不同批次样品之间无法进行横向对比确定其实际差异值。而绝对含量不受不出峰物质的影响,对于微量物质也能进行定量。在实际的生产应用中,需要确定各成分的绝对含量来进行精油的生产和质量控制。
精油的成分分析主要采用GC-MS进行鉴定和定量。采用SIM模式的GC-MS较常规的全扫描模式能够显著降低信号噪音,提供更高的峰检测灵敏度和准确性,不检测不产生指定离子的外溶物质,具有一定程度的选择性的优点[16]。因此,建立GC-MS/SIM法同时测定山苍子精油中主要成分绝对含量的方法,为山苍子精油的质量控制和进一步的开发利用提供依据。
-
正己烷为色谱纯,对照品:α-蒎烯(纯度:99%)、D-柠檬烯(纯度:95%)、β-蒎烯(纯度:95%)均购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;山苍子精油,1,8-桉叶素(99%)、香茅醛(纯度:96%)、芳樟醇(纯度:98%)、柠檬醛(纯度:95%)均购自上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
-
Agilent 7890A-5975C气相色谱质谱联用仪;;电子天平(d=0.1 mg,METTLER TOLEDO 公司)
-
精密称取α-蒎烯1.81 mg、β-蒎烯1.94 mg、D-柠檬烯8.25 mg、1,8-桉叶素2.02 mg、香茅醛5.16 mg、芳樟醇4.87 mg、柠檬醛26.38 mg,将7种对照品置于同一10 mL容量瓶中,用正己烷定容至刻度,摇匀。
-
精密称取山苍子精油100 μL(8.84 mg)于10 mL容量瓶中,用正己烷定容至刻度,摇匀,即得。
-
气相色谱条件:采用 HP-5MS 色谱柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm),起始温度设置 50℃,保持3 min,以2 ℃·min−1升至65 ℃,保持2 min,再以4 ℃·min−1升至150 ℃。进样口温度150 ℃,载气为高纯氦气,氦气流速为1.5 mL·min−1,分流比100∶1,进样量1.0 μL。质谱条件:EI源,离子源温度230 ℃,四极杆温度150 ℃,溶剂延迟3 min。使用 NIST 谱库图谱进行检索。7种成分定量采用SIM模式,SIM参数见表1。
成分 分子式 CAS号 保留时间(min) 选择离子(m/z) α-蒎烯 C10H16 7785-70-5 5.666 93/91/77 β-蒎烯 C10H16 127-91-3 7.250 93/91/69 D-柠檬烯 C10H16 5989-27-5 9.727 68/67 1,8桉叶素 C10H18O 470-82-6 9.813 43/81/108 芳樟醇 C10H18O 78-70-6 14.221 71/93/41 香茅醛 C10H18O 2385-77-5 16.955 69/41/95 橙花醛 C10H16O 5392-40-5 20.925 69/41/94 香叶醛 C10H16O 5392-40-5 22.163 69/41/84 Table 1. Retention time and SIM parameters for seven components
-
精密吸取“1.3.1”项下的混合对照品溶液,用倍比稀释法稀释,配制成系列浓度梯度溶液。按“1.3.3”下条件进行GC-MS分析。
-
精密吸取“1.2.1”项下混合对照品溶液,按“1.3.3”下GC-MS条件连续进样6次,测定峰面积。
-
在一定线性关系范围内,准确吸取精油100 μL于10 mL容量瓶,用正己烷定容至刻度, 摇匀后即得供试品溶液。取6份供试品溶液按“1.3.3”下GC-MS条件进行分析。
-
按“1.3.2”项下制备供试品溶液,取同一供试品溶液按“1.3.3”GC-MS条件分别于0、2、4、6、8、12 h时进样,考察方法的稳定性。
-
精密称取已知含量的山苍子精油0.884 mg,依次加入α-蒎烯、β-蒎烯、D-柠檬烯、1,8-桉叶素、芳樟醇、香茅醛、柠檬醛对照品,称得质量分别为1.5、2.1、8.4、1.4、1.2、1.3、35.5 mg,将其置于10 mL容量瓶中,用正己烷定容至刻度,吸取6份按“1.3.3”下GC-MS条件进行分析,计算其回收率。
-
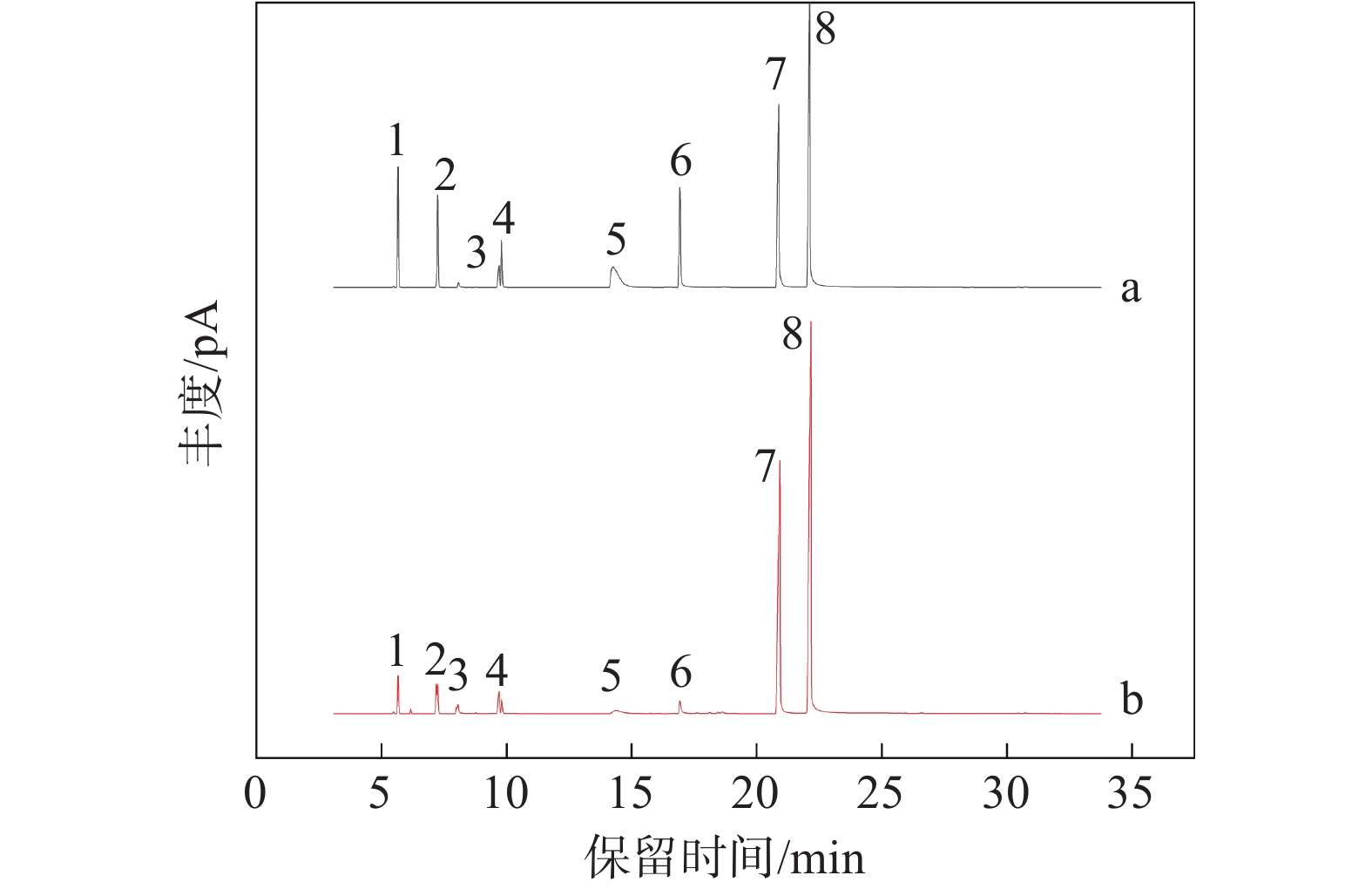
山苍子精油及其对照品选择离子色谱图见图1。
-
以色谱峰面积(A)为纵坐标,进样浓度(C)为横坐标绘制标准曲线,结果见表2。各目标化合物标准曲线相关系数R2均大于0.999,表明在一定范围内线性关系良好,。
成分 回归方程 R2 线性范围(mg·mL−1) α-蒎烯 Y=35339450X+890610 0.9995 0.0283−1.81 β-蒎烯 Y=3026162X+723400 0.9996 0.0303−1.94 D-柠檬烯 Y=2068990X+575560 0.9993 0.0039−8.25 1,8-桉叶素 Y=15288160X+476980 0.9993 0.0316−2.02 芳樟醇 Y=20393910X−511690 0.9996 0.0761−4.87 香茅醛 Y=16502240X+309310 0.9997 0.0806−5.16 柠檬醛 Y=16501700X+2874190 0.9992 0.6622−26.38 Table 2. Regression equations, correlation coefficients(R2) and linear ranges of the seven measured components
-
由表3可知,7种被测成分精密度的相对标准偏差在1.74%~2.76%之间,重复性的相对标准偏差在0.98%~2.40%之间,稳定性试验的相对标准偏差在0.99%~2.86%之间。结果表明仪器稳定、精密度良好,方法重复性良好,供试品溶液在12 h内稳定。
成分 RSD(%) 精密度 重复性 稳定性 α-蒎烯 1.74 0.99 2.86 β-蒎烯 2.20 1.23 2.77 D-柠檬烯 2.46 1.23 2.59 1,8-桉叶素 1.83 1.14 1.10 芳樟醇 2.58 2.40 2.23 香茅醛 2.01 2.37 2.34 柠檬醛 2.76 0.98 0.99 Table 3. Precisions, repeatabilities and stabilities of the determination of the seven measured components
-
7种被测成分的平均加标回收率为93.40%~107.35% ,表明大部分目标化合物都被成功地回收并检测到,分析方法准确度高。结果见表4。
成分 未加标平均峰面积(A) 浓度(mg·mL−1) 加标平均峰面积(A) 浓度(mg·mL−1) 平均回收率(%) α-蒎烯 2605785.33 0.0490 7534990.83 0.1899 93.93 β-蒎烯 2292761.67 0.0546 8773755.83 0.2800 107.35 D-柠檬烯 2436279.17 0.9569 4074828.00 1.8285 103.77 1,8-桉叶素 1218350.67 0.0490 3261755.00 0.1840 96.44 芳樟醇 1299372.33 0.0906 3539511.33 0.2027 93.40 香茅醛 1295897.50 0.0623 3311974.33 0.1895 97.89 柠檬醛 86989689.67 5.3657 141856005.17 8.8656 98.59 Table 4. recoveries for seven measured components
-
按“1.3.2”项下方法制备供试品溶液,按“1.3.3”项下GC-MS条件进行测定,按外标法计算山苍子精油中α-蒎烯、β-蒎烯、D-柠檬烯、1,8-桉叶素、芳樟醇、香茅醛、柠檬醛的绝对含量。结果见表5。采用峰面积归一化法确定其相对含量。初始积分阈值决定了峰数目多少与面积总和,最终影响到主含量高低。由表6可知:输入不同的初始阈值,相对含量有所差异,甚至初始阈值大于15,芳樟醇的峰未被保留,导致其他成分的相对含量值增加。与外标法测定得到的绝对含量进行对比,柠檬醛的相对含量偏高,而α-蒎烯、β-蒎烯、D-柠檬烯、1,8-桉叶素和香茅醛的相对含量偏低。
成分 绝对含量mg·g−1 α-蒎烯 5.55 β-蒎烯 6.17 D-柠檬烯 108.25 1,8-桉叶素 5.54 芳樟醇 10.25 香茅醛 6.92 柠檬醛 604.14 Table 5. Absolute content of the seven measured ingredients
成分 峰面积归一化法(不同阈值) 外标法 13.00 14.00 15.00 α-蒎烯 2.50 2.54 2.63 0.56 β-蒎烯 2.20 2.23 2.30 0.62 D-柠檬烯 2.32 2.35 2.43 10.82 1,8-桉叶素 1.18 1.19 1.22 0.55 芳樟醇 1.38 1.29 — 1.02 香茅醛 1.31 1.27 1.21 0.69 柠檬醛 85.37 85.74 87.11 60.41 Table 6. External standard method and peak area normalization method(%)
-
经比较,采用外标法和峰面积归一化法计算精油中有关组分的含量,各有优缺点。采用峰面积归一化法计算相对含量,操作简单,无需对照品,但在设定初始阈值时,会根据样品的特点和分析目的来进行主观设定,这对峰面积归一化法的计算结果造成很大影响。外标法可准确计算主成分绝对含量值,但需要使用多种对照品建立标准曲线,同时进样量要求十分准确,样品的测试需严格控制在与标准物相同的操作条件下进行。因此,在精油的成分分析中,可根据不同的分析要求,以及分析成本、分析效率选择分析方法。山苍子精油组分相对复杂,本试验建立的GC-MS/SIM法同时测定山苍子精油中主要成分的绝对含量,符合方法学验证要求,可为山苍子精油内部组分的研究以及精油质量控制提供参考。
Simultaneous determination of the absolute contents of major components in Litsea cubeba essential oil by GC-MS/SIM
doi: 10.12172/202311090001
- Received Date: 2023-11-09
- Available Online: 2024-03-05
-
Key words:
- Litsea cubeba essential oil /
- GC-MS /
- selective ion monitoring (SIM)
Abstract: In order to investigate the absolute contents of the main components in Litsea cubeba essential oil, a gas chromatography mass spectrometry/selective ion monitoring (GC-MS/SIM) was established for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the main components (α--pinene, β--pinene, D-limonene, 1, 8-cineole, linalool, citronellal, citral) were analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively. The method is simple and efficient, and the components in Litsea cubeba essential oil were well separated within 25 min. The linearity of the method was good over a certain range (R2> 0.999), and the precision, stability and reproducibility were all in accordance with the requirements, with the average recoveries of 93.40%-107.35%. The results showed that the method meets the requirements of methodological validation, and can be used for the determination of the multi-component content of Litsea cubeba essential oil and provide a basis for its quality evaluation.





















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: