-
绣球“无尽夏”(Hydrangea macrophylla 'Endless Summer')引种于意大利,与其他种类八仙花最大的区别在于花期的长短,其花期比普通八仙花平均要长10—12周,是作为鲜切花、“永生花”加工最好的材料之一,并且耐低温能力强,在较冷的环境中也能开花,但其具不孕性,主要采用无性繁殖技术繁殖。针对绣球扦插繁殖技术,目前有相关的学者进行了相应的研究,薛玉剑[1]研究了不同基质配比对绣球扦插生根的影响,得出泥炭土利于绣球插穗的生根;朱玮[2]从激素处理对扦插生根的影响做了研究,得出300 mg/L的IBA 溶液处理利于插穗生根;乔谦等[3]对比不同品种绣球的扦插效果,得出大花绣球品种为皮部生根型,大花绣球成活率明显高于圆锥绣球和乔木绣球;潘月[4]从生长调节剂和基质配比上研究其对大叶绣球扦插生根的影响,得出IBA促进插穗生根,混合基质比单一基质对插穗生根效果更佳。综上,目前对绣球扦插繁殖技术的研究主要是集中在基质和生长调节剂的使用对绣球基质扦插生根的影响,而对绣球“无尽夏”水培扦插繁殖的技术鲜有报道,仅李秋荔[5]对无尽夏品种的基质扦插进行了研究。利用设备控制下水培的扦插方式,以设备提供人工创设的根系环境来替代自然的土壤环境,通过物联网技术实现扦插环境水、肥、光、气、热的精确自动调节,营养水平均衡,避免不利于生长的土壤条件的干扰和影响,降低病死率,实现绣球扦插苗周年生产,并提高根系的生长速度及根系量。水培的三大技术即营养液膜技术(浅水培)、深液流法(深水培)和气雾培均有其各自优缺点,本次试验以大花绣球“无尽夏”为研究对象,在静止水培条件下探讨不同水培设备种类(水培技术)、不同生根剂种类及不同生根剂浓度对绣球“无尽夏”扦插生根的影响,通过生长指标对比分析,得出最佳的水培技术、生根剂种类及浓度,为后续绣球“无尽夏”的工厂化育苗及其余绣球品种的水培扦插提供参考依据和技术支撑。
-
试验地位于福建林业职业技术学院园林园艺产业学院的无土栽培区,温室外年平均气温19.3℃,日平均光照时间达10 h,温室内光照条件充足。温室内白天温度15—30℃,空气相对湿度50—90%,温室内夜间温度15—20℃,空气相对湿度在30—85%。扦插期间,每天10点至16点开启温室的湿帘和风机保持通风,11点至15点期间开启内外双层遮阳网。
-
绣球“无尽夏”盆栽来自闽侯县廷坪乡汶合村良地自然村,并置于福建林业职业技术学院园林园艺产业学院的花卉产业生产基地的温室大棚中养护。采集生长状况一致,无病虫害健壮的植株外围的半木质化枝条。枝条顶部留2片叶,并将叶片剪除3/5,枝条粗度为0.5—1.0 cm,长度10 cm左右,带1—2个节,上切口距上芽1 cm左右平剪,下切口呈马蹄形斜剪。剪取下来的枝条按100根/捆的数量绑扎后提前浸泡于清水中待用。
-
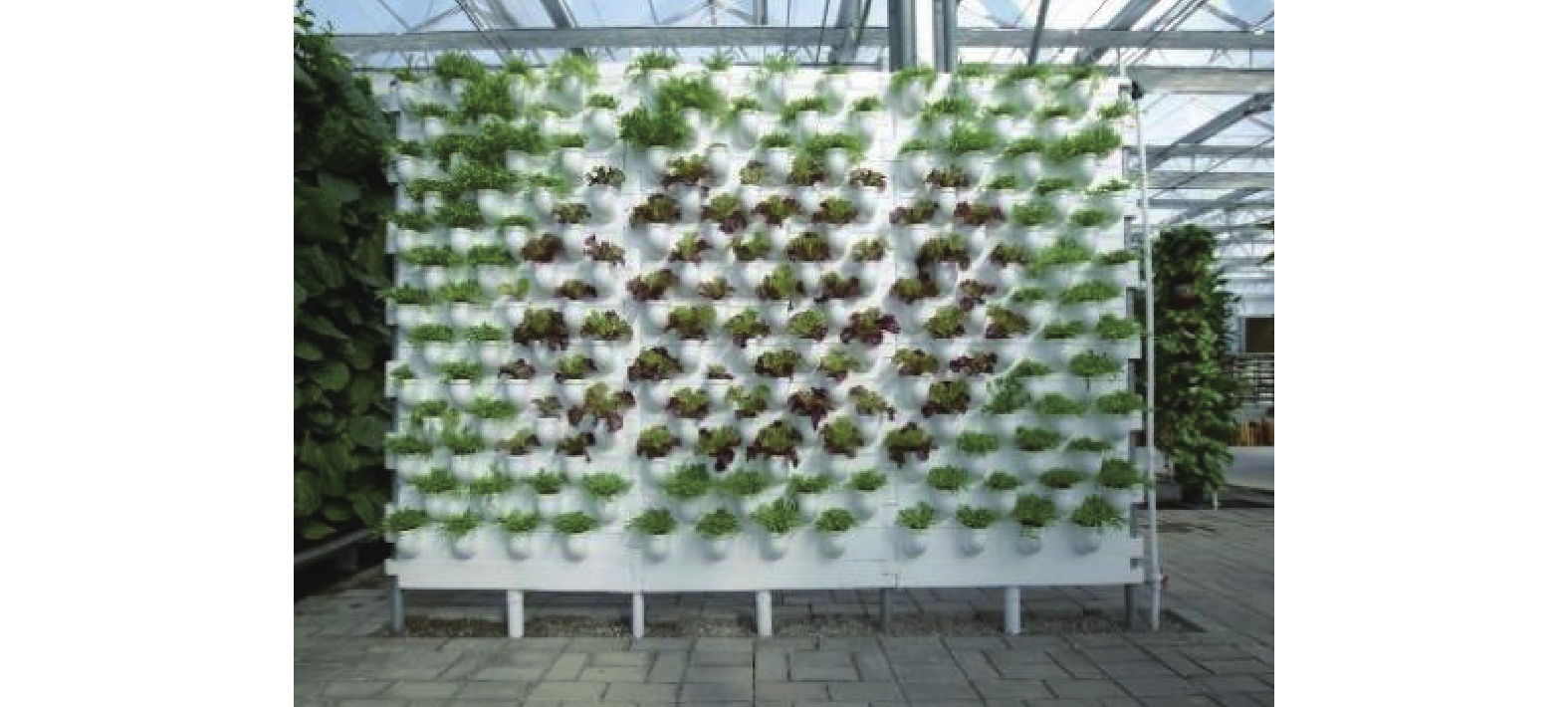
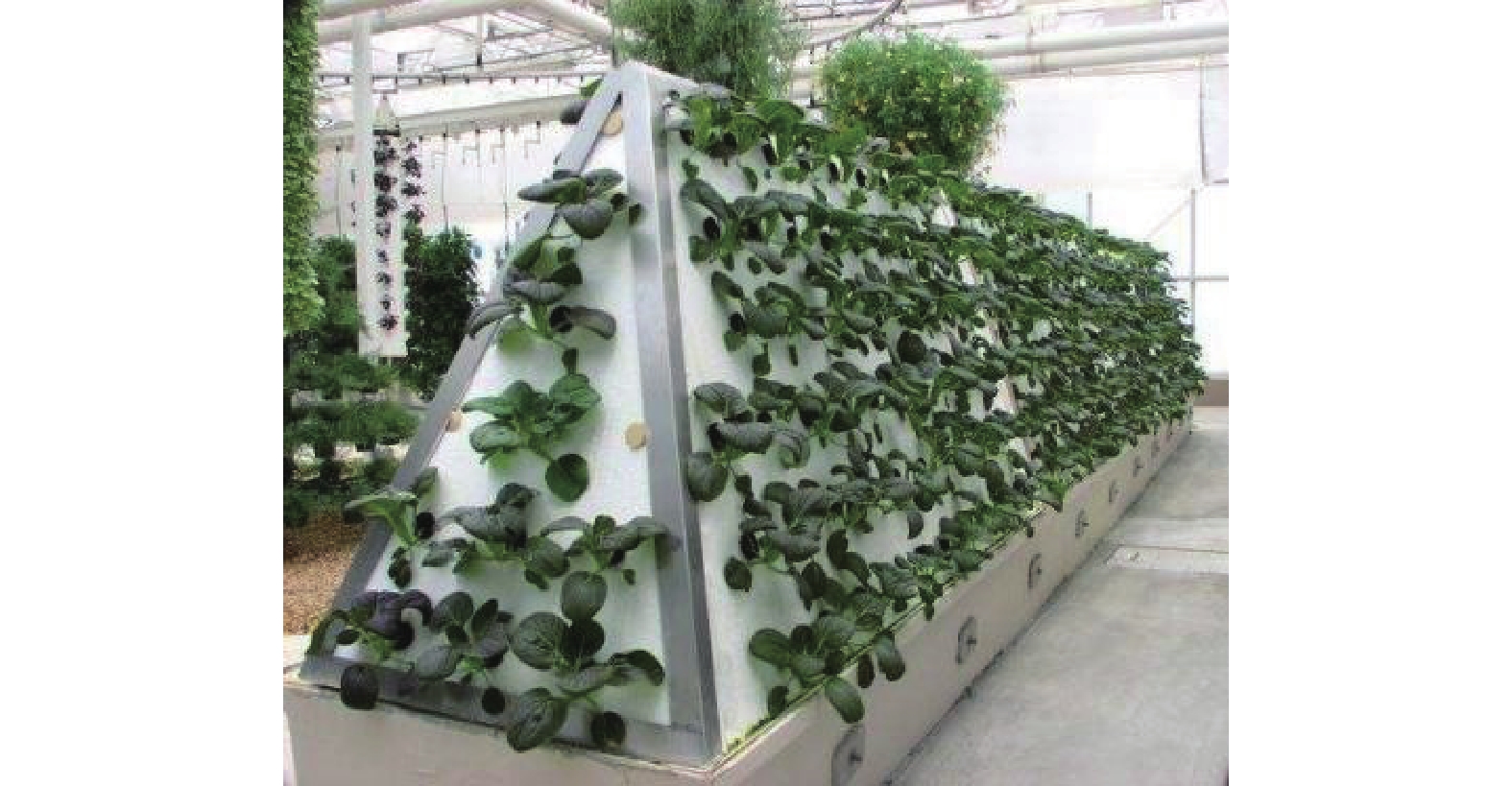
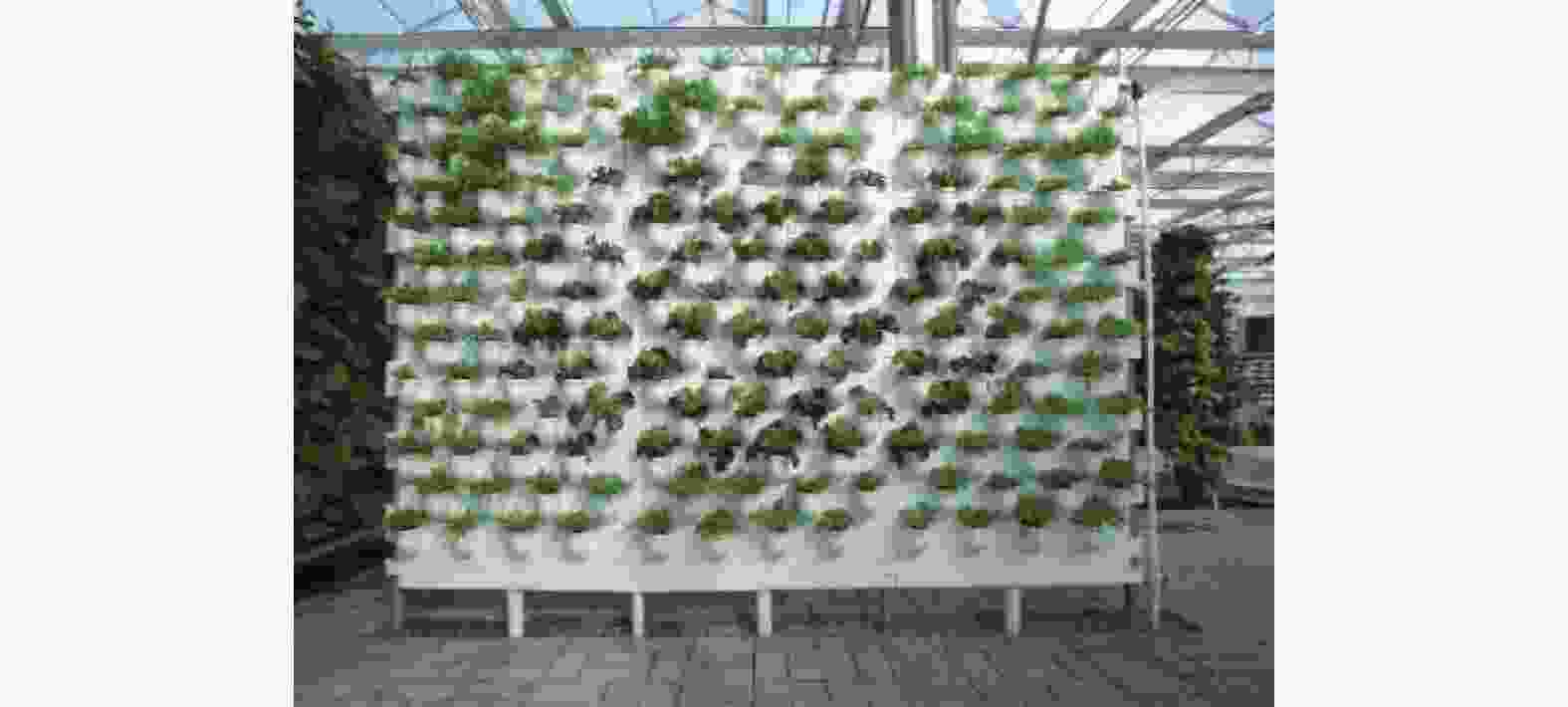
采用4因素3水平试验设计方法(表1和表2),探讨不同水培设备种类(气雾培模式“A型”结构—图1、NFT模式单层平铺结构—图2、DFT深液流栽培蔬菜墙—图3)、不同生根剂种类(NAA、ABT、IBA)及不同生根剂浓度(100 mg·L−1、300 mg·L−1、500 mg·L−1)对绣球“无尽夏”扦插生根的影响,穗条在不同生根液中均处理5 min,每种处理30根扦插枝条,重复3次。水培系统中的营养液配方是一致的,即A液为:150 kg水+15 kg大量复合肥,B液为:150 kg水+2 kg中微量复合肥+2 kg硫酸钾,其中大量元素复合肥为阿康·氮磷钾16-16-16);中微量元素为沃点·硼锌铁钙镁。
因子 因子标签 水平1 水平2 水平3 水培设备种类 A 气雾培模式“A型”结构 NFT模式单层
平铺结构DFT深液流
栽培蔬菜墙生根剂种类 B NAA ABT IBA 生根剂浓度(mg/L) C 100 200 300 空白 CK Table 1. Four-factor and three-level orthogonal experiment design
处理号 水培设备种类 生根剂
种类生根剂浓度
(mg/L)空白
对照1 DFT深液流栽培蔬菜墙 ABT 300 1 2 DFT深液流栽培蔬菜墙 IBA 100 2 3 NFT模式单层平铺结构 NAA 300 2 4 NFT模式单层平铺结构 IBA 200 1 5 NFT模式单层平铺结构 ABT 100 3 6 气雾培模式“A型”结构 IBA 300 3 7 气雾培模式“A型”结构 NAA 100 1 8 DFT深液流栽培蔬菜墙 NAA 200 3 9 气雾培模式“A型”结构 ABT 200 2 Table 2. List of different experiment treatment
-
水培扦插后每天观察插穗生根时间,记录最早生根时间,扦插40 d后,观察每种处理3组重复试验所得的插条的平均生根率(%)、平均根系长度(cm)及平均根系数量(条)。生根率(%):生根穗条/扦插穗条×100%;平均根系量(条):随机取3次重复试验每种处理的成活苗10株测量其根系总量并取平均值;平均根系长度(cm):随机取3次重复试验每种处理扦插成活苗10株测量其根系长度总和并取平均值。
试验结果运用Excel进行数据整理统计,并利用SPSS 20.0进行方差分析及多重比较分析。因素对扦插生长指标的影响通过单因素方差和Tukey事后比较进行分析。
-
据表3可知,处理9即将插穗用200 mg·L−1的ABT生根剂浸泡5 min后置于气雾培模式“A型”结构中培养,平均生根率高达96.7%,且扦插苗长势好,根系旺,叶片多且大,根系的平均长度及根系量均最佳;而处理8即将插穗用200 mg·L−1的NAA生根剂浸泡5 min后,置于DFT深液流栽培蔬菜墙上培养,其生根效果极差,仅有43.3%生根率,大部分穗条褐化枯死,即便生根,其苗木长势差,根量少且短,叶片泛黄。观察发现,处理4即用200 mg·L−1的IBA生根剂浸泡5 min后置于NFT模式单层平铺结构中培养根系萌发最早,处理3即用300 mg·L−1的NAA生根剂浸泡5 min后置于NFT模式单层平铺结构中培养最迟,两者前后差距8 d。对无尽夏绣球因变量最早生根时间进行主体间效应检验得表4,据表4可知,不同处理对绣球水培扦插最早生根时间的影响因素中生根剂种类对其扦插生根达0.05的显著性水平,其次是生根剂浓度,水培设备的影响差异不显著。
处理 生根
数/枝平均生根
率/%平均根系
长度/cm平均根系
量/条最早生根
时间/d扦插苗长势情况 1 66 73.3 8.3 15.3 16 扦插苗长势一般,根系量一般,叶片长势较弱,
根系中等,根系较短2 50 55.6 7.2 12.3 12 扦插苗长势差,插穗基部褐化情况严重,
成活率低,叶片长势弱,根系短3 72 80.0 11.6 9.7 18 扦插苗长势较差,根系量少,叶片弱小,根系长度较长 4 75 83.3 12.5 17.1 10 扦插苗长势一般,根系量中等,叶片比较小,根系长度较长 5 77 85.6 13.3 24.7 15 扦插苗长势较好,根系旺盛,叶片长势中等,根系长度较长 6 84 93.3 15.1 18.3 11 扦插苗长势好,根系较旺盛,叶片中等,根系长度长 7 81 90.0 14.8 11.5 15 扦插苗长势好,根系量一般,叶片中等,根系长度较长 8 39 43.3 9.5 8.3 16 扦插苗长势差,插穗枯死率高,成活率极低,
根系量一般,叶片极小且泛黄,根系短9 87 96.7 15.4 25.2 14 扦插苗长势好,根系旺盛,叶片多且大,根系长度长 Table 3. Growth of cutting seedlings of Hydrangea macrophylla 'Endless Summer'
因变量: 最早生根时间 源 III 型平方和 df 均方 F Sig. 校正模型 53.333a 6 8.889 11.429 0.083 截距 1792.111 1 1792.111 2304.143 0.000 水培设备 2.889 2 1.444 1.857 0.350 生根剂种类 46.222 2 23.111 29.714 0.033 生根剂浓度 4.222 2 2.111 2.714 0.269 误差 1.556 2 0.778 总计 1847.000 9 校正的总计 54.889 8 a. R 方 =0 .972(调整 R 方 = 0.887) Table 4. Test of inter-subjective effect
-
对绣球“无尽夏”的因变量平均生根率进行主体间效应检验及极差分析,得出表5和表6。由表5可知,不同处理对绣球水培扦插的平均生根率的影响因素中水培设备种类对其扦插生根达0.05的显著性水平,其次是生根剂种类,生根剂浓度的影响差异不显著。从表6可知,据极差R值大小,不同因素对插条生根率影响的主次关系为因素A水培设备种类>因素B生根剂种类>因素C生根剂浓度。据K值(表示每种因素试验结果总和)大小可直观得出,绣球“无尽夏”在A1B2C3组合处理下,生根效果最佳,即用300 mg·L−1的ABT生根剂浸泡5 min后置于气雾培模式“A型”结构中培养。该最佳组合不属于本次正交试验设计其中的一个处理方式,但与本试验的处理9即采取200 mg·L−1的ABT生根剂浸泡5 min后置于气雾培模式“A型”结构中培养的处理方式除了生根剂浓度外,有两种因素是一致的,这也进一步表明生根剂浓度并非影响扦插生根率的最主要因素。
因变量: 平均生根率 源 III 型平方和 df 均方 F Sig. 校正模型 2445.273a 6 407.546 8.134 0.114 截距 54615.690 1 54615.690 1090.061 0.001 水培设备种类 2052.327 2 1026.163 20.481 0.047 生根剂种类 299.340 2 149.670 2.987 0.251 生根剂浓度 93.607 2 46.803 0.934 0.517 误差 100.207 2 50.103 总计 57161.170 9 校正的总计 2545.480 8 a. R 方 =0 .961(调整 R 方 = 0.843) Table 5. Test of inter-subjective effect
处理号 A水培设
备种类B生根
剂种类C生根
剂浓度平均生
根率/%1 3 2 3 73.3 2 3 3 1 55.6 3 2 1 3 80.0 4 2 3 2 83.3 5 2 2 1 85.6 6 1 3 3 93.3 7 1 1 1 90.0 8 3 1 2 43.3 9 1 2 2 96.7 求和 K1 280.00 213.33 231.11 K2 248.89 255.56 223.33 K3 172.22 232.22 246.67 均值 k1 93.33 71.11 77.04 k2 82.96 85.19 74.44 k3 57.41 77.41 82.22 极差 R 35.93 14.07 7.78 因素影响主次 A>B>C 最优方案 A1B2C3 Table 6. Analysis of orthogonal test results on the influence of various factor levels on the average rooting rate
-
对绣球“无尽夏”的因变量平均根系长度进行主体间效应检验及极差分析,得出表7和表8。由表7可知,不同处理对绣球水培扦插的影响因素中水培设备种类亦对根系长度的生长影响达0.05的显著性水平,生根剂浓度和生根剂种类的影响差异不显著。从表8可知,据极差R值大小,不同因素对插条根系伸长生长影响的主次关系为因素A水培设备种类>因素C生根剂浓度 >因素B生根剂种类。据K值大小可直观得出,绣球“无尽夏”在A1B2C2组合处理下,根系长度的伸长生长效果最佳,即本试验中的处理9用200 mg·L−1的ABT生根剂浸泡5 min后置于气雾培模式“A型”结构中培养。
因变量: 平均根系长度 源 III 型平方和 df 均方 F Sig. 校正模型 71.753a 6 11.959 10.280 0.091 截距 1288.810 1 1288.810 1107.860 0.001 水培设备种类 69.807 2 34.903 30.003 0.032 生根剂种类 0.807 2 0.403 0.347 0.743 生根剂浓度 1.140 2 0.570 0.490 0.671 误差 2.327 2 1.163 总计 1362.890 9 校正的总计 74.080 8 a. R 方 =0 .969(调整 R 方 = 0.874) Table 7. Test of inter-subjective effect
处理号 A水培设
备种类B生根
剂种类C生根
剂浓度平均根系
长度/cm1 3 2 3 8.3 2 3 3 1 7.2 3 2 1 3 11.6 4 2 3 2 12.5 5 2 2 1 13.3 6 1 3 3 15.1 7 1 1 1 14.8 8 3 1 2 9.5 9 1 2 2 15.4 求和 K1 45.30 35.90 35.30 K2 37.40 37.00 37.40 K3 25.00 34.80 35.00 均值 k1 15.10 11.97 11.77 k2 12.47 12.33 12.47 k3 8.33 11.60 11.67 极差 R 6.77 0.73 0.80 因素影响主次 A>C>B 最优方案 A1B2C2(处理9) Table 8. Analysis of orthogonal test results on the influence of various factor levels on the average root length
-
对绣球“无尽夏”扦插苗的因变量根系量进行主体间效应检验及极差分析,得出表9和表10。由表9可知,不同处理对绣球水培扦插根系量的影响因素中生根剂种类对根系量的生长影响达0.05的显著性水平,其次为水培设备种类,而生根剂浓度的影响差异不显著。从表10可知,据极差R值大小,不同因素对插条根系量的增长影响的主次关系为因素B生根剂种类>因素A水培设备种类>因素C生根剂浓度。据K值大小可直观得出,绣球“无尽夏”在A1B1C1组合处理下,根系量的增加效果明显,即本试验中的处理7用100 mg·L−1的NAA生根剂浸泡5 min后置于气雾培模式“A型”结构中培养。
因变量: 平均根系量 源 III 型平方和 df 均方 F Sig. 校正模型 290.793a 6 48.466 10.579 0.089 截距 2253.084 1 2253.084 491.821 0.002 水培设备种类 68.936 2 34.468 7.524 0.117 生根剂种类 212.442 2 106.221 23.187 0.041 生根剂浓度 9.416 2 4.708 1.028 0.493 误差 9.162 2 4.581 总计 2553.040 9 校正的总计 299.956 8 a. R 方 =0 .969(调整 R 方 = 0.874) Table 9. Test of inter-subjective effect
处理号 A水培设
备种类B生根
剂种类C生根
剂浓度平均根系
数量/条1 3 2 3 15.3 2 3 3 1 12.3 3 2 1 3 9.7 4 2 3 2 17.1 5 2 2 1 24.7 6 1 3 3 18.3 7 1 1 1 11.5 8 3 1 2 8.3 9 1 2 2 25.2 求和 K1 55.00 29.50 48.50 K2 51.50 65.20 50.60 K3 35.90 47.70 43.30 均值 k1 18.33 9.83 16.17 k2 17.17 21.73 16.87 k3 11.97 15.90 14.43 极差 R 6.37 11.90 2.43 因素影响主次 B>A>C 最优方案 A1B1C1 Table 10. Analysis of orthogonal test results on the influence of various factor levels on the average root number
-
因生长环境条件影响,植物在水培环境中,根系容易发生“病变”问题,如烂根、缺水枯萎等。DFT深液流栽培蔬菜墙的优点是不怕中途停水停电,根际的缓冲作用大,稳定性好,利于带根系植物的生长和管理,但对设施装置的要求高,根际氧气的补充十分重要,一旦染上土传病害,蔓延快,危害大,且若遇高温天气停电,则高温对根系生长的影响大,因根系泡于高温水中,容易发生烂根现象。NFT模式水培植物底部接触浅液流吸水吸肥,上部暴露在湿气中吸氧,较好地解决了根系吸水与吸氧的矛盾,但液流浅、液温不稳定,一旦停电停水,植株易枯萎,根际环境稳定性差等。气雾培可很好地解决根系氧气的供应,几乎不会出现由于根系缺氧而生长不良现象,养分及水分利用率高,但若遇断电,作为一个封闭的系统,如控制不当,根系病害易于传播、蔓延。周全卢等[6]试验发现气雾培条件下可加快打开植物气孔,增加蒸腾速率、水分运输,为根系营造良好的生长空间和提高充足氧气,从而增加光合产物合成;王谢等[7]得出气雾培条件下能避免淹水胁迫和和养分分布不均对桑树生根的影响;Rietveld[8]研究发现加拿大短叶松在气雾培条件下,其根系生长速度比土壤扦插繁殖快。本试验结果得出,水培设备的种类是影响绣球扦插生根率和根系长度最重要因素,且气雾培模式“A型”结构是水培扦插繁殖最佳设备,而DFT深液流栽培蔬菜墙不利于绣球扦插生根,该试验结果与设备本身的特性相关,且与上述研究学者得出的结论相吻合。
-
试验结果表明,不同生根剂种类对绣球扦插生根情况影响中,对最早生根时间和平均根系数量的影响显著,ABT处理后扦插苗的所有生根最佳,IBA处理加快不定根产生,令其生根时间早于ABT,但经ABT处理后的植株生长状况最佳,这也表明生根时间早与植物后期的生长状况并无直接联系。同时,低浓度NAA利于绣球根系量的增长。无尽夏绣球属皮部生根型[9],ABT属于一种新型、无毒、高效、广谱型植物生根促进剂,其能补充植物生根所需外源生长素并促进内源生长素合成的双重功能[10],能使不定根原基分生组织细胞分化,呈簇状爆发性生根,同时,亦有相关研究指出IBA是长效化合物,在空气中分解速度慢、毒性小,而NAA生理活性高、毒性较IBA大[11]。综上,本试验研究结果与上述结论有一定相似性,ABT利于绣球内源激素的合成并能促进不定根的生长,而NAA总体而言,因其生理活性高,毒性较大,所以其处理的插穗基部褐化情况明显,植物扦插成活率及生根效果较差,仅在低浓度处理时,利于根系的生长。同时,植物激素浓度的高低虽对绣球的扦插生根影响不显著,但通过多变量正交试验分析发现,高浓度水平利于生根率的提高,中等浓度水平利于早生根及平均根系长度伸长及根量的增加,总体上,低浓度水平对各扦插生根因子的影响程度为中等。
Study on the Hydroponic Cutting Technique of Hydrangea macrophylla ‘Endless Summer’
doi: 10.12172/202301170001
- Received Date: 2023-01-17
- Available Online: 2023-10-11
- Publish Date: 2023-12-28
-
Key words:
- Hydrangea macrophylla 'Endless Summer' /
- Hydroponics /
- Cuttage
Abstract: Taking Hydrangea macrophylla ‘Endless Summer’ as the research object, the effects of different types of hydroponics equipment, different types and concentrations of rooting agents on cutting rooting of Hydrangea macrophylla ‘Endless Summer’ were studied under static hydroponics conditions. Through the comparative analysis of growth indicators, the best hydroponic cutting rooting scheme was summarized, providing reference basis and technical support for the subsequent factory seedlings of Hydrangea macrophylla ‘Endless Summer’ and hydroponic cutting of other Hydrangea varieties. The effects of different types of hydroponic equipment, rooting agents and concentrations of rooting agents on the earliest rooting time, average rooting rate, average root length and average root quantity of Hydrangea macrophylla ‘Endless Summer’ hydroponic cuttings after rooting were studied by using a four-factor and three-level experimental design. In the treatment 9, the cuttings were soaked with 200 mg·L−1 ABT rooting agent for 5 min and then cultured in the "A type" structure of the aerosol culture mode, the growth of the cuttings was the best. In the treatment 8, the cuttings were soaked with 200 mg·L−1 NAA rooting agent for 5 min and then cultured on the DFT deep-flow culture vegetable wall, the rooting effect was the worst. In the treatment 4, the cuttings were soaked with 200 mg·L−1 IBA rooting agent for 5 min and then cultured in the NFT single-layer flat structure, the root germination time was the earliest. In the treatment 3, the cuttings were soaked in 300 mg·L−1 NAA rooting agent for 5 min, and then cultured in NFT mode single-layer flat structure, the rooting was the latest. The types of rooting agents were the most important factor affecting the earliest rooting time and root quantity in hydrangea hydroponics cutting results, and the type of hydroponics equipment was the most important factor affecting the average rooting rate and root length growth, among which the "A type" structure of the aerosol culture mode was the best for cutting and rooting. Among different rooting agents, IBA was the most beneficial to the early rooting time, but ABT was the most beneficial to the growth of cuttings, and low concentration of NAA was the most beneficial to the increase of root mass. The concentration of rooting agent did not affect the rooting rate of Hydrangea macrophylla 'Endless Summer' hydroponic cutting.























 DownLoad:
DownLoad:

