-
朱红毛斑蛾(Phauda flammans Walker),隶属于鳞翅目(Lepidoptera)斑蛾科(Zygaenidae),是榕属植物(Ficus spp.)上的寡食性食叶害虫,主要危害小叶榕,垂叶榕等[1]。榕属植物是我国南方城市重要绿化树种,在城市道路,公园,小区中广泛种植,非常易于朱红毛斑蛾繁殖与扩散[2]。在厦门,自2016年首次监测到朱红毛斑蛾危害,每年的危害呈上升趋势,朱红毛斑蛾每年发生三代,常间歇性暴发危害,严重时甚至能将整株榕树叶片食光,严重影响市容市貌[3]。
在城市园林绿化的防治上,生物农药具有低毒的特性,是一种环保型农药。加大园林绿化中生物农药的使用,能有效地保护植物免受病虫害的侵扰的同时,还能保护城市生态环境,推动城市生态文明建设[4]。
通过比较四种常用生物农药,甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐(以下简称甲维盐)、苏云金杆菌、球孢白僵菌和棉铃虫核型多角体病毒对朱红毛斑蛾的毒杀效果,以期筛选出高效低毒的生物农药,为有效防治朱红毛斑蛾提供科学依据。
-
采集厦门市湖里区垂叶榕树梢朱红毛斑蛾幼虫带回实验室,用新鲜的垂叶榕叶片进行饲养。3 d后筛选生理状态一致的3—5龄幼虫,随机分装至养虫盒(0.5 L),按10头/盒进行后续药效试验。
-
甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐水分散粒剂(甲氨基阿维菌素5%,河北中保绿农作物科技有限公司),苏云金杆菌悬浮剂(Bt,8000 IU/μL,乳山韩威生物科技有限公司),球孢白僵菌水分散粒剂(球孢白僵菌400亿孢子/g,山西绿海农药科技有限公司),棉铃虫核型多角体病毒悬浮剂(棉铃虫核型多角体病毒20亿 PIB/mL,河南勇冠乔迪农业科技有限公司)。
-
根据预实验结果,将甲维盐水分散粒剂稀释成5000,10000,2000,40000,80000倍液,苏云金杆菌悬浮剂稀释成100,200,500,1000,2000倍液,球孢白僵菌水分散粒剂,棉铃虫核型多角体病毒悬浮剂稀释成500,1000,2000,3000,4000倍液,清水为对照。将每盒幼虫置于新鲜垂叶榕枝条上,用手持微型喷雾器均匀喷洒各浓度药液与清水,每处理设置3个重复。处理后的试虫置于恒温光照箱(温度25±1℃、相对湿度70±5%、光照光周期L∶D=16∶8 h)饲养和观察。记录药后1 d—10 d每处理死亡虫数,体视镜下观察试虫对外界刺激没有反应,视为虫体死亡,试验方法参考自NYT 1154.9—2008部标。[5]。
-
试验数据通过Excel软件进行整理与分析,通过公式Ⅰ,公式Ⅱ计算不同处理下试虫死亡率与校正死亡率。对统计数据进行毒力回归分析,毒力回归方程式为:Y=aX+b, 相关系数为r、通过公式Ⅲ~Ⅵ计算半致死浓度(LC50)和LC50的95%置信区间[6,7]。
公式Ⅰ:
公式Ⅱ:
公式Ⅲ:
$ \mathrm{Z}={\left(2\mathrm{\pi }\right)}^{-1/2}{\mathrm{e}}^{-1/2(Y-5)} $ ;公式Ⅳ:
$ \omega=Z^2/PQ $ ,ω是权重系数,P死亡率,Q=(1-P);公式Ⅴ:
$ {SE}_{\left(m\right)} $ 是m的标准误,m是lg(LC50),$ \overline{x} $ 为浓度对数平均值,n为某浓度供试总虫数;公式Ⅵ:LC50的95%置信限:
$ {10}^{\left(\mathrm{l}\mathrm{g}\right({\mathrm{L}\mathrm{C}}_{50})\pm 1.96\times {SE}_{\left(m\right)})} $ -
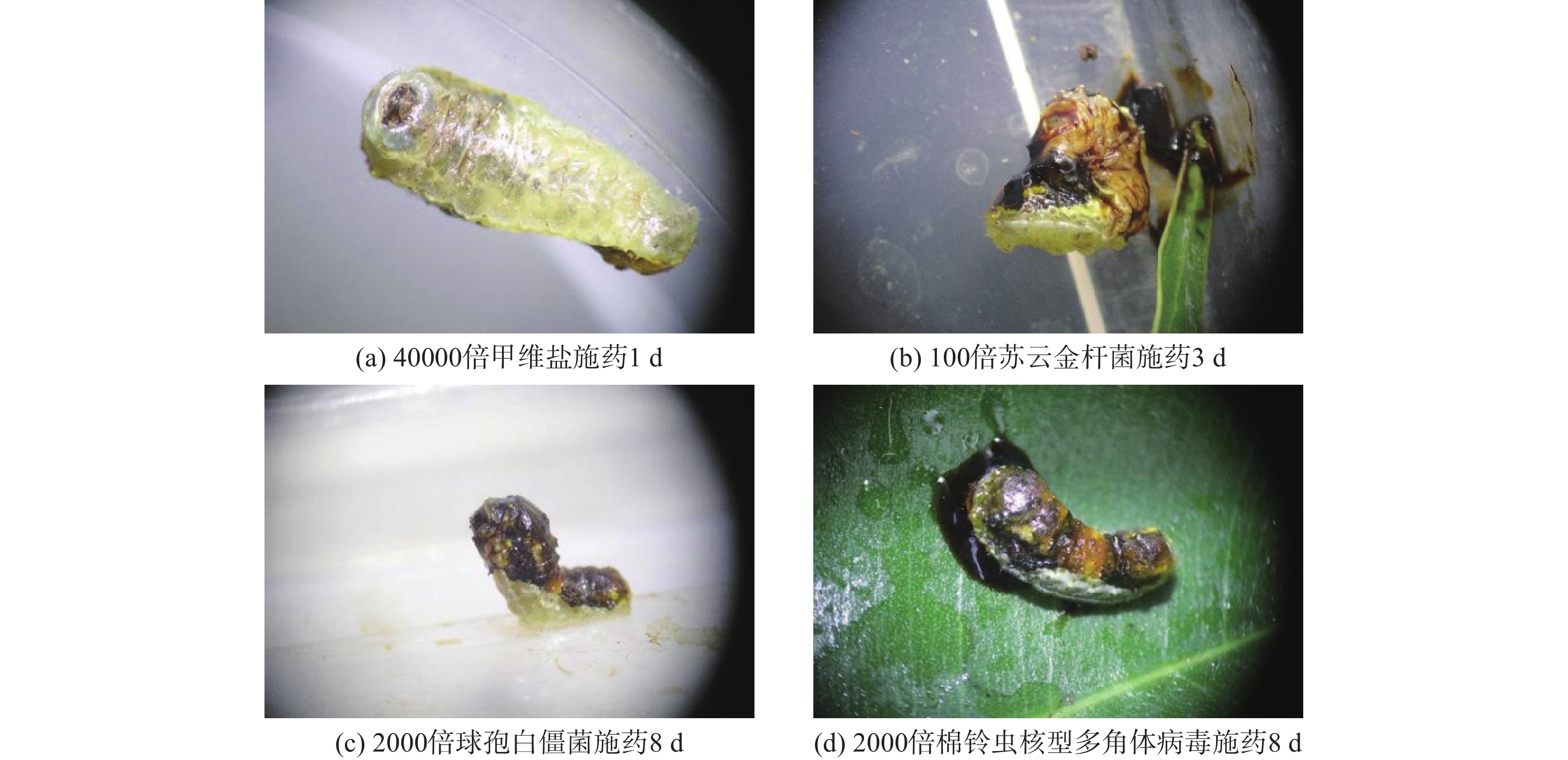
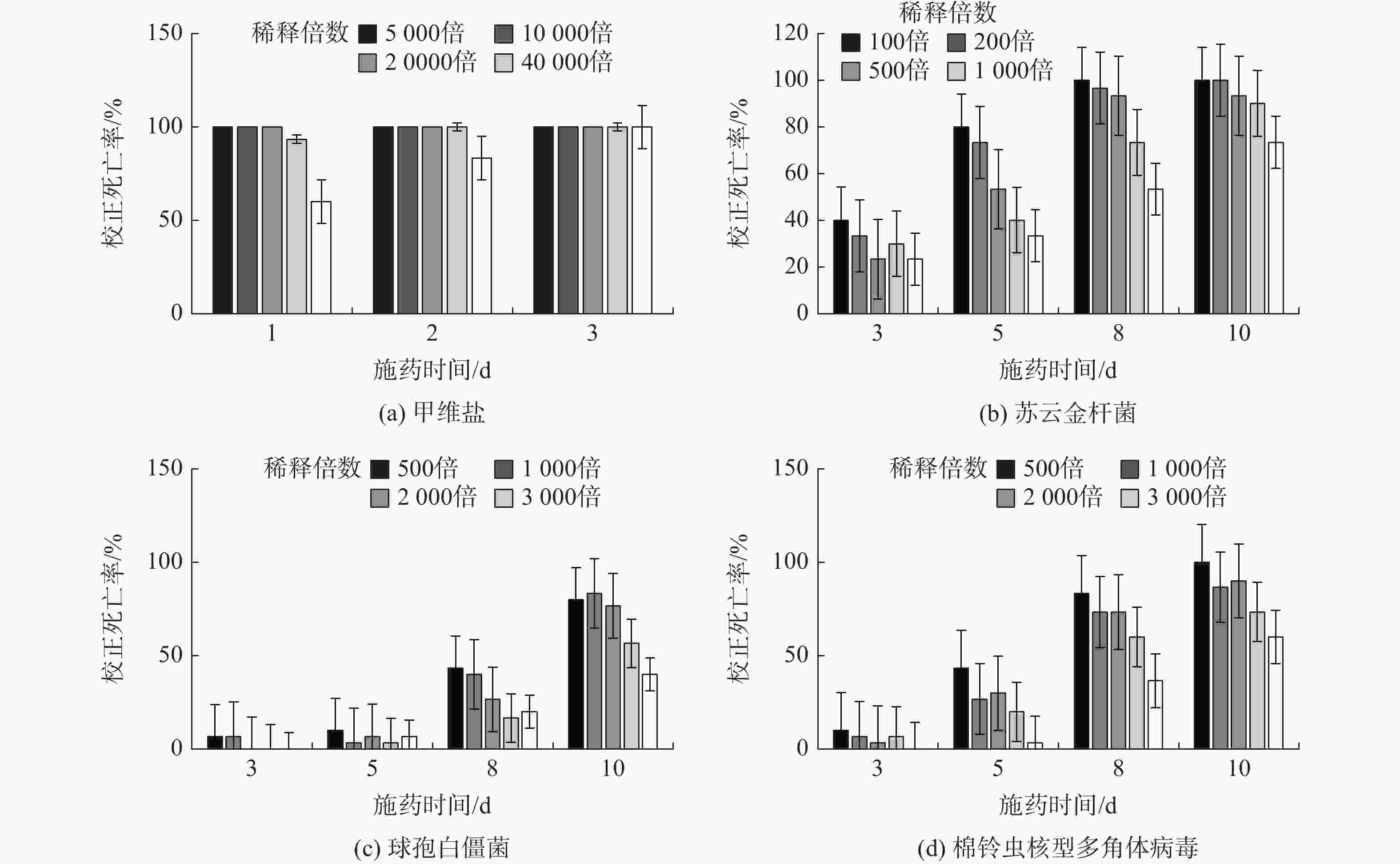
甲维盐处理1 d后有明显的致死率,80000倍处理下的幼虫校正死亡率达到了60%,3 d后所有试虫死亡。各浓度处理下所有龄期的试虫麻痹作用显著,用药后基本停止进食,在体视镜下仅有少数试虫能对外界刺激能做出反应,连续观察至虫体死亡后,均未能恢复移动或进食。苏云金杆菌处理下,试虫中毒症状明显,第2 d后出现明显的体液外渗,头微伸出,身体逐渐溶解,拒食,处理3 d后,不断有试虫开始死亡,但死亡率均未超过50%,5 d后死亡率明显上升。球孢白僵菌处理下,防治效果最差,5 d后试虫未出现明显中毒症状,8 d后逐渐开始拒食,部分幼虫头部抬起,并不断有试虫死亡,处理10 d后最高死亡率仍未过90%,且仍有部分试虫未出现症状。棉铃虫核型多角体病毒处理下,5 d后开始出现症状,进食量明显减少,吐出红色体液,8 d后症状加剧,死亡率攀升,各农药处理后的症状见图1。各处理校正死亡率与时间的关系见图2。
-
4种生物农药的毒力测定结果见表1。从表中可以看出,甲维盐综合毒力最高,施药1 d后LC50为10.859 mg/L,其余三种农药效果都不显著;施药5 d后药剂毒力苏云金芽孢杆菌>棉铃虫核型多角体病毒>球孢白僵菌,其中球孢白僵菌无明显药效,施药8 d后,药剂毒力棉铃虫核型多角体病毒(LC50:269.286 mg/L)>苏云金芽孢杆菌(LC50:419.436 mg/L)>球孢白僵菌(LC50:2581.854 mg/L)。施药10 d后,3种药剂毒力都显著增强,药剂毒力棉铃虫核型多角体病毒(LC50:121.140 mg/L)>苏云金芽孢杆菌(LC50:166.619 mg/L)>球孢白僵菌(LC50:233.848 mg/L)。
药剂 施药时间 毒力方程 相关系数 LC50(mg/L) 95%置信区间 甲维盐 1 d y=0.707+4.145x 1 10.859 8.77—13.445 苏云金芽孢杆菌 3 d y=3.394+0.321x 0.827 99725.017 18223.236—545736.18 5 d y=1.693+1.042x 0.992 1492.504 937.051—2377.211 8 d y=0.2+1.83x 0.975 419.436 293.136—600.153 10 d y=1.759+1.459x 0.960 166.619 96.985—286.249 球孢白僵菌 8 d y=1.899+0.909x 0.946 2581.854 1473.304—4524.506 10 d y=2.203+1.181x 0.839 233.848 152.398—358.829 棉铃虫核型多角体病毒 5 d y=0.315+1.396x 0.815 2269.372 1540.443—3343.227 8 d y=2.081+1.201x 0.886 269.286 177.952—407.499 10d y=2.022+1.429x 0.797 121.140 79.132—185.45 Table 1. Toxicity of four biological pesticides on Phauda flammans
-
本试验采用喷雾法进行农药筛选,能够充分地模拟养护过程中的喷药环境,试验结果具有较强的指导意义。从本次的试验结果可以看出,4种生物农药对朱红毛斑蛾的幼虫的防治均具有一定的效果,农药的速效性甲维盐>苏云金芽孢杆菌>棉铃虫核型多角体病毒>球孢白僵菌,农药的持效性甲维盐>棉铃虫核型多角体病毒>苏云金芽孢杆菌>球孢白僵菌。综合来看,甲维盐是防治朱红毛斑蛾最合适的高效低毒农药,具有在城市园林绿化养护中推广的价值。
目前对朱红毛斑蛾防控多以化学农药为主,生物农药中对虫生真菌研究较多。在蒋璐等的研究中,试验了苏云金杆菌72 h的致死率,杀虫效果不理想,可能是与其作用速度较慢有关;在陈学敏的研究中可以看出市售球孢白僵菌致病力不及分离自朱红毛斑蛾幼虫僵虫的球孢白僵菌PfBb。甲维盐24 h毒力超过大部分化学试剂,是一种非常优良的生物农药[8-11]。
使用的4种生物农药,尤其是甲维盐,还可开展进一步的田间试验与农药的共毒研究,能更好地对朱红毛斑蛾的防控提供指导作用。另外,还可结合朱红毛斑蛾天敌昆虫的物候期,研究这些农药对其影响,以期做到适度防控,科学防控,进一步实现绿色生态文明建设。
Screening of Biological Pesticides for Controlling Phauda flammans
doi: 10.12172/202212270001
- Received Date: 2022-12-27
- Available Online: 2023-10-12
- Publish Date: 2023-12-28
-
Key words:
- Phauda flammans /
- Biological control /
- Efficacy test /
- Half lethal concentration (LC50)
Abstract: In order to screen effective and low toxic biological pesticides, the laboratory efficacy test of four biological pesticides against the 3-5 instar larvae of Phauda flammans was carried out. The results showed that the four biological pesticides showed obvious toxicity to Phauda flammans, and the toxicity of abamectin-aminomethyl was the strongest. It had obvious toxicity after 1 day at 80000 times the concentration, and the LC50 was 10.859 mg/L. The LC50 of Bacillus thuringiensis, HearNPV and Beauveria bassiana were 166.619 mg/L, 121.140 mg/L and 233.848 mg/L after 10 days, 5 days and 8 days, respectively. From the perspective of the quick effect of pesticides, the content of abamectin-aminomethyl>Bacillus thuringiensis>HearNPV>Beauveria bassiana. From the perspective of the persistence of pesticides, the content of abamectin-aminomethyl>HearNPV>Bacillus thuringiensis>Beauveria bassiana. To sum up, abamectin-aminomethyl was the most appropriate pesticide with high efficiency and low toxicity for the control of Phauda flammans.


























 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
